Eye on the Horizon: The $79B Evolution of Ophthalmic Therapies
January 22, 2026
The ophthalmic (eye-care) landscape is currently undergoing its most significant regulatory and therapeutic transformation in a decade. As the FDA moves away from retrospective, probabilistic testing toward a proactive Quality Revolution, the criteria for market entry have fundamentally shifted. Sponsors are now tasked with balancing hyper-speed innovation—such as the “biosimilar tsunami” and the explosion of AI-driven home monitoring—against a regulatory bar that is higher and more deterministic than ever before.
This edition of PharmaFocus explores the critical intersection of CMC precision, clinical breakthroughs in retinal disease, and the digital frameworks that will define the $79.4 billion ophthalmic market through 2033. From the EMA’s progressive “stepwise equivalence” to the FDA’s new “Essentially Free” standard for particulates, we provide the regulatory intelligence necessary to navigate this high-stakes environment.
The Quality Revolution: FDA’s New Paradigm for Topical Ophthalmic Products
Precipitated by widespread recalls of contaminated OTC eye drops between 2023 and 2024, the FDA has fundamentally shifted its oversight from retrospective testing to proactive sterility assurance. The guidance Quality Considerations for Topical Ophthalmic Drug Products (2023), has since become the industry’s compliance gold standard, prohibiting reliance on probabilistic sterility testing and mandating deterministic verification to address supply chain vulnerabilities.
Microbiological Considerations and Container Closure Integrity (CCI): The Agency now views traditional sterility testing as insufficient for detecting low-level contamination or intermittent seal failures.
- Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT): Manufacturers are expected to implement non-destructive, deterministic CCIT (LOD ≤ 20 microns) in stability protocols, replacing or augmenting destructive sterility tests.
- Preservative-Free Systems: For multidose preservative-free (MDPF) systems, the container tip must be engineered to prevent microbial backflow (ingress protection). The use of silver sulfate as a preservative is explicitly discouraged due to safety concerns.
Visible Particulate Matter – The “Essentially Free” Standard: The FDA has moved toward a zero-tolerance approach for extrinsic matter in ophthalmic topicals, diverging from the probabilistic limits (AQLs) allowed for injectables under USP <790> and <1790> .
- Inspection Technologies: For opaque containers, where manual visual inspection is impossible, the guidance mandates the use of technologies such as X-ray spectroscopy or destructive testing to identify particulates.
- Thresholds: The industry must move toward robust defect libraries and 100% inspection processes where feasible to meet the “essentially free” standard.
Regulatory Observation: The Quality Considerations guidance is not merely a recommendation; it is a gateway to approval. Sponsors failing to provide robust CCIT validation, particulate defect libraries, or justification for preservative systems face immediate refuse-to-file (RTF) actions or Complete Response Letters (CRLs). Industry observers have noted a sharp increase in Information Requests (IRs) related to these CMC aspects during the review of both NDAs and ANDAs.
Streamlining Generics: The pH Adjuster Waiver Policy
While the FDA has tightened quality standards, it has simultaneously sought to reduce unnecessary regulatory burdens for generic developers through the finalization of the guidance Considerations for Waiver Requests for pH Adjusters in Generic Drug Products Intended for Parenteral, Ophthalmic, or Otic Use (2025).
- The Barrier Removed: Historically, strict Q1/Q2 sameness rules meant that even minor differences in buffers, acids, or bases could trigger requirements for costly in vivo clinical studies, as these were not considered exception excipients.
- The New Pathway: Sponsors can now bypass clinical endpoint studies by demonstrating physicochemical comparability. If side-by-side data (e.g., pH, osmolality, buffer capacity) proves the formulation difference impacts neither safety nor efficacy, a waiver is scientifically justified. This policy lowers the barrier to entry for complex ophthalmic generics, shifting the burden of proof from the clinic to the bench.
Regulatory Observation: By removing the need for in vivo bioequivalence studies for minor formulation deviations, companies can accelerate development timelines. However, the scientific justification must be robust. Sponsors are advised to generate comprehensive side-by-side physicochemical data packages early in development to support these waiver requests within the ANDA Module 3.
Global Harmonization: The EMA’s Equivalence Guideline
Across the Atlantic, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has implemented a transformative framework, the Guideline on quality and equivalence of locally applied, locally acting cutaneous products, that is arguably more progressive than the FDA’s current stance on complex generic bioequivalence. While titled for “cutaneous” products, their principles have broad implications for ophthalmic products (ointments, gels, emulsions).
The Stepwise Equivalence Approach
- Pharmaceutical Equivalence: Demonstration that the Test and Reference products have the same qualitative and quantitative composition (Q1/Q2) and similar microstructure (Q3).
- In Vitro Release Testing (IVRT): Proving that the drug is released from the formulation matrix at the same rate as the reference.
- In Vitro Permeation Testing (IVPT): Using relevant biological models (e.g., ex vivo corneal tissue or synthetic membranes) to demonstrate equivalent drug delivery to the target site.
Regulatory Observation: This guideline represents a massive opportunity for cost savings. Previously, demonstrating equivalence for a generic ophthalmic emulsion (like a cyclosporine generic) often required large, expensive, and insensitive clinical trials with therapeutic endpoints. The EMA now accepts robust in vitro data as a surrogate for clinical efficacy. Developers of ophthalmic ointments and gels can now bypass Phase 3-like equivalence trials if they can validate their IVRT/IVPT methods.
Therapeutic Breakthroughs: The “Year of the Retina”
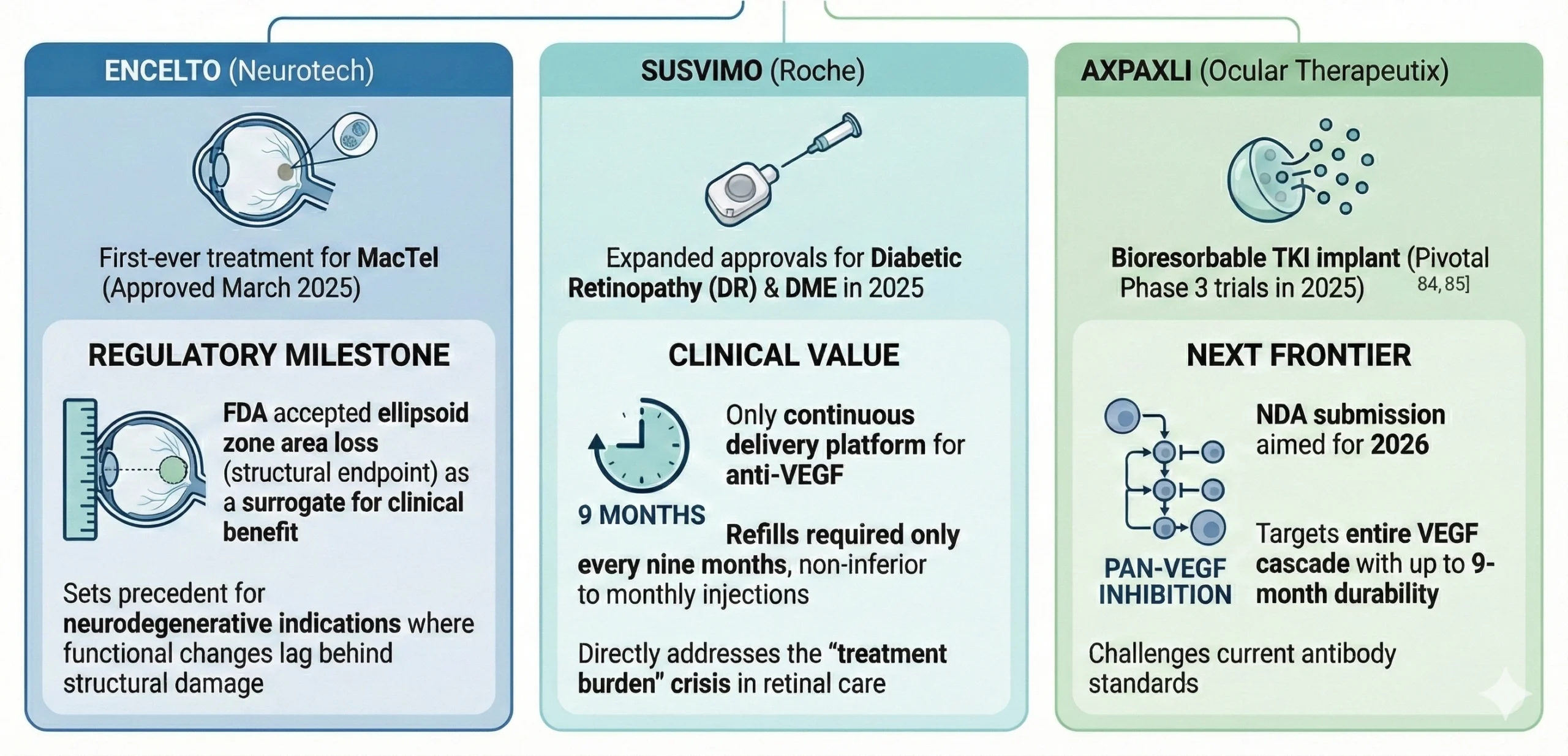
The Biosimilar Wave: Reshaping Market Economics
The expiration of exclusivity for Eylea (aflibercept) has triggered a biosimilar tsunami, fundamentally altering the commercial landscape for retinal drugs. Between 2024 and 2025, the FDA approved six aflibercept biosimilars. Among these, Yesafili (Biocon) and Opuviz (Samsung Bioepis) achieved the coveted “interchangeable” designation, allowing pharmacy-level substitution without prescriber intervention.
Launch Dynamics: Litigation vs. At-Risk Market entry has been bifurcated by BPCIA litigation strategies:
- Settled Launches (2026): Biocon (Yesafili) and Sandoz (Enzeevu) have settled with Regeneron for launches in the second half of 2026.
- At-Risk Launch: Amgen (Pavblu) disrupted the landscape by launching “at-risk” in late 2024, aggressively capturing early market share despite ongoing patent disputes.
Strategic Implications: The influx of these products is driving significant price erosion in the $9 billion anti-VEGF sector. Payers are responding with aggressive “step edits,” requiring biosimilar failure before authorizing branded therapies like Eylea HD or Vabysmo, forcing manufacturers to compete on value rather than just clinical differentiation.
Regulatory Setbacks: Lessons in Evidence
Not all endeavors meet with success. The regulatory rejections experienced by Outlook Therapeutics and Aldeyra Therapeutics offer critical case studies.
- Outlook Therapeutics’ ONS-5010 (Lytenava) received a third CRL in December 2025 for its ophthalmic bevacizumab formulation. The FDA cited a lack of “substantial evidence of effectiveness,” requiring confirmatory evidence beyond the single pivotal trial (NORSE TWO). This underscores that 505(b)(2) applications cannot rely solely on common knowledge of off-label efficacy; they must independently meet statistical rigor. Interestingly, the EMA approved ONS-5010, highlighting a divergence where European regulators placed more weight on the totality of bevacizumab’s known profile.
- Aldeyra Therapeutics faced a protracted review for reproxalap (dry eye disease), receiving a PDUFA extension to March 2026. The challenge lies in demonstrating efficacy in both signs (objective, e.g., fluorescein staining) and symptoms (subjective, e.g., patient-reported dryness) of Dry Eye Disease (DED). While chamber studies showed symptom relief, the FDA required replication in “adequate and well-controlled” field studies, which have proven difficult to validate due to patient heterogeneity.
The Digital Horizon: AI and Home Monitoring
The integration of AI into ophthalmology has matured from technical validation to regulatory reality, driven by new device categories and lifecycle frameworks.
- Home Monitoring: The FDA’s 2024 De Novo authorization of Notal Vision’s Scanly Home OCT established a new product code for patient-operated diagnostics, enabling daily AI-driven monitoring of wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) fluid dynamics from home.
- Autonomous Screening: The sector continues to scale with Digital Diagnostics (LumineticsCore) and Eyenuk (EyeArt) expanding deployment. Notably, AEYE Health received FDA clearance in May 2024 for the first portable autonomous Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) screening system, significantly lowering barriers to entry.
- Regulatory Flexibility: The FDA’s final guidance on Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCP) for AI/ML-enabled devices (Dec 2024) allows sponsors to pre-specify algorithm retraining protocols. This critical evolution enables AI models to learn and improve post-market without triggering repetitive 510(k) submissions.
Future Outlook: The Road to 2035
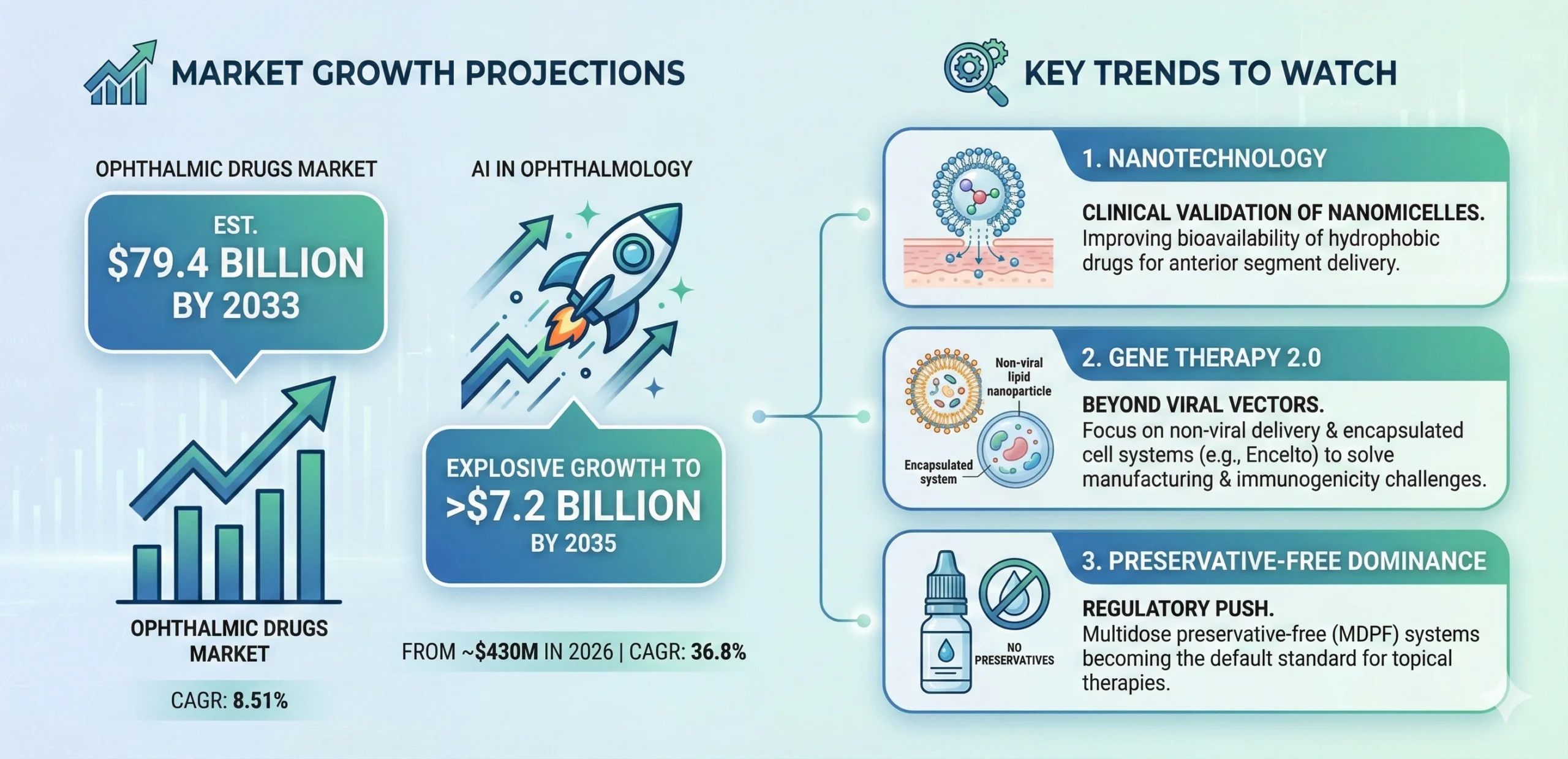
The future of ophthalmology is bright, but the regulatory bar is higher than ever. Success requires a blend of scientific boldness and regulatory precision—qualities that define the modern landscape.
How Can BLA Regulatory Help?
BLA Regulatory functions as a strategic extension of your team, providing the technical leadership and end-to-end expertise needed to transform complex eye-care innovations into successful global approvals. Our ex-FDA and industry CMC and clinical experts are specifically equipped to help you navigate the industry’s new deterministic standards, from implementing robust CCIT protocols and particulate defect libraries to designing validated IVRT/IVPT studies that bypass costly clinical endpoints.
By bridging the gap between scientific boldness and regulatory precision, we ensure your IND, NDA, or BLA submissions—whether for novel retinal gene therapies or AI-enabled monitoring devices—meet the highest standards of sterility assurance and clinical rigor. From initial gap analysis to post-approval lifecycle management, BLA Regulatory provides the clear, actionable strategies necessary to succeed in today’s heightened regulatory environment.
References
- FDA Guidance: Quality Considerations for Topical Ophthalmic Drug Products
- Neurotech Pharmaceuticals: Encelto BLA Approval Press Release
- Genentech: FDA Approves Susvimo for Diabetic Retinopathy
- BiologicsHQ: FDA Approves First Two Interchangeable Eylea Biosimilars
- EMA: Guideline on Quality and Equivalence of Locally Applied, Locally Acting Cutaneous Products
- Outlook Therapeutics: Regulatory Update on ONS-5010
- Aldeyra Therapeutics: Complete Response Letter for Reproxalap
- Eyes On Eyecare: Notal Vision’s At-Home OCT for Wet AMD
- Grand View Research: Ophthalmic Therapeutics Market Analysis
- Towards Healthcare: AI in Ophthalmology Market Sizing
- FDA Guidance: Waiver Requests for pH Adjusters in Generic Drug Products
- GaBI Online: Biosimilars Approved in the US

